Automotive Part Marking 101 | Component Traceability

The number of parts used to make a single car has doubled in the last 10 years. As cars get more complex, it’s harder to track parts through inventory, production, and the car’s entire life. More


The number of parts used to make a single car has doubled in the last 10 years. As cars get more complex, it’s harder to track parts through inventory, production, and the car’s entire life. More


Choosing the right laser marking tool can be overwhelming, especially with the numerous laser technologies and marking options available. From fiber laser sources to CO₂ and green lasers, each has its strengths, and your choice directly impacts the quality of marking, material compatibility, and the long-term success of your operation.
If you’re working in industrial laser marking, whether you’re an engineer, a production manager, or a manufacturing professional, it’s essential to know what matters most for your application.
Are you seeking deep, durable marks that meet stringent regulatory standards, or is speed and precision your top priority?
Each type of laser marking offers unique advantages depending on your goals, and making the right choice starts with understanding your options.
We’ll break down the different types of laser marking, including three primary laser technologies and two key subtypes. As well as how to select the best laser marking source for your specific needs, with tips on choosing the right material and achieving the required marking depth for compliance and optimal performance.
Laser part marking is a standard practice in several industries due to its effectiveness in long-term part identification and its compliance with the rigorous standards set forth for aerospace, mechanical, and other high-demand sectors.
However, each industry has specific needs regarding the product, as well as potential damage that can occur if the wrong laser is used. The equipment you need is just one part of the process; however, first, you’ll want to consider which laser is best suited for your application.
There are five standard lasers for laser marking:
CO2 laser marking is a popular laser engraving and marking solution because of its ability to mark non-metallic materials. It’s efficient in marking a variety of non-metals, too, including:
The CO2 laser produces an infrared laser beam and uses CO2 gas as the active medium. The laser is emitted at 10.6 micrometers and features high beam quality, allowing it to focus laser power into a small spot and produce high-quality laser marks. This laser has the longest wavelength, which falls within the invisible infrared spectrum.
This laser is efficient for cutting some materials and for personalizing products. However, this type of laser also requires more maintenance and uses more energy.
Another laser source is fiber laser marking, which also enables the accurate marking of non-metallic surfaces. The fiber laser source operates at a shorter wavelength than a CO2 laser, utilizing a fiber optic laser device to emit laser beams at a wavelength of 1.064 micrometers. The wavelength produced falls within the infrared spectrum.
It quickly and accurately produces laser marks on materials such as:
This laser source also offers the ability to be tuned for specific applications with easily adjustable settings.
A fiber laser can also be used for embossing or to add discoloration where desired. The discoloration process with a fiber laser offers a range of colors and improved control simultaneously.
The fiber laser is the most commonly used in the laser marking industry, particularly common in aerospace, metallurgy, automotive, and mechanical applications. It’s helpful for all types of metals and has a longer lifespan compared to other lasers.
The YAG laser operates at a wavelength similar to that of the fiber laser (1.064 micrometers). However, this type of laser has a different structure from a fiber laser, and the beam passes through multiple crystals to create the beam.
The YAG laser is ideal for marking metals and plastics in its more widely recognized configuration. However, it can also be adjusted to mark more sensitive materials.
The green laser, the first subtype of the YAG laser, is the only laser with a wavelength in the visible spectrum. This allows manufacturers to mark many sensitive materials, such as:
The green laser is ideal for these sensitive materials because its wavelength is located near the UV spectrum, which generates less heat.
The UV laser is another subtype of the YAG laser. Thanks to implanted crystals, it became possible to adjust the wavelength for this laser and utilize others, providing access to the only laser in the invisible ultraviolet spectrum (0.355 micrometers).
The UV laser has the shortest wavelength used in the laser marking field and, as such, is relied upon for markings on fairly sensitive materials.
This laser also enables the execution of “cold markings”, allowing manufacturers to avoid part degradation due to heat. This laser is used for marking solar panels, electrical components, and other parts that require a refined approach.
Planning the production of your next line involves numerous considerations. These include the materials you will use and the expected completion time for products.
Meanwhile, several of those factors also influence the choice of laser:
With the variety of materials used in production, it makes sense to prioritize the materials when considering a laser source. For more heat-sensitive materials, it is important to find the right laser and access one that is easily adjustable.
The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a measure of the reliability of your laser based on its operating hours. Each laser has a different expectation, and please note that these are average times, not guaranteed lifespans. Some lasers have a longer MTBF but can fail in a shorter period than expected.
While the fiber laser has a Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) of 100,000 hours, CO2 lasers have a significantly shorter MTBF of 30,000 hours. This is a crucial factor to consider when selecting the best option for your production cadence.
Some lasers are singled out for the ability to make deeper marks than others. For specific regulations and standards, the laser with a deeper marking capability would be the preferred choice.
Meanwhile, other materials require a lighter mark that doesn’t cause damage. Therefore, the depth of the mark is a significant factor in selecting a laser source.
Some lasers require more maintenance than others. This means a commitment of more of the budget and possible interference with production timelines if maintenance is needed frequently.
Your production timeline is important for both your revenue and to help your clients meet their own projected deadlines. As such, the marking process needs to be completed promptly.
Note: Depending on the material to be marked, the correct laser source can significantly impact meeting the timeline and avoiding delays caused by lengthy marking processes.
Resource: If laser marking isn’t the answer at all, there’s always dot peen marking.
In some industries, the laser will need to be adjusted for separate part lines or stages in the production process. In such cases, it is more cost-effective to find a laser that can be easily adjusted. This facilitates effective marking on the desired timeline more effectively.
With three laser marking types and two subtypes, it should be a reasonable process to narrow down the best laser for an application based on the factors involved. Your production line requires a specific type of mark, and you expect how long that mark will last.
The right laser marking source means faster delivery of products that carry distinct markings to fit your clients’ needs.
If you have questions about the right laser source for your project, it’s time to talk to our experienced Technomark staff. Reach out today, and we can help point you in the right direction.
(Editor’s note: This blog was originally published in January 2023 and was updated recently to reflect the most up-to-date information.)


Every part tells a story.
In manufacturing, that story is written with precision and permanence. From serial numbers to intricate barcodes, part markings ensure every component can be identified, traced, and trusted throughout its lifecycle. But how do you choose the right system to deliver these critical marks?
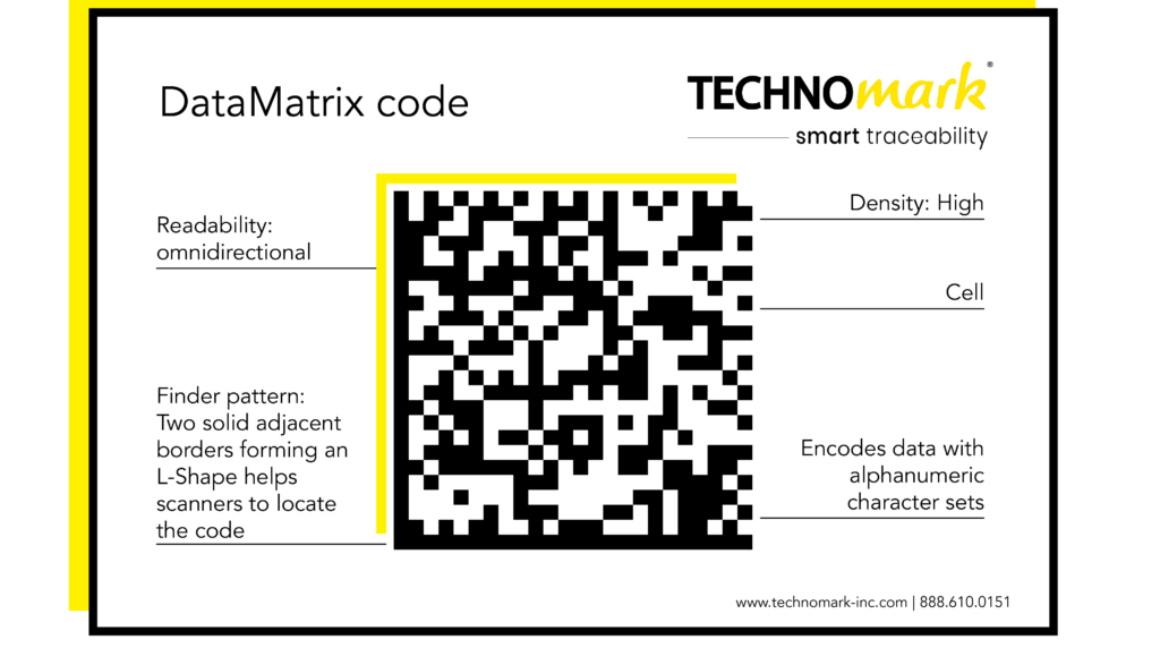
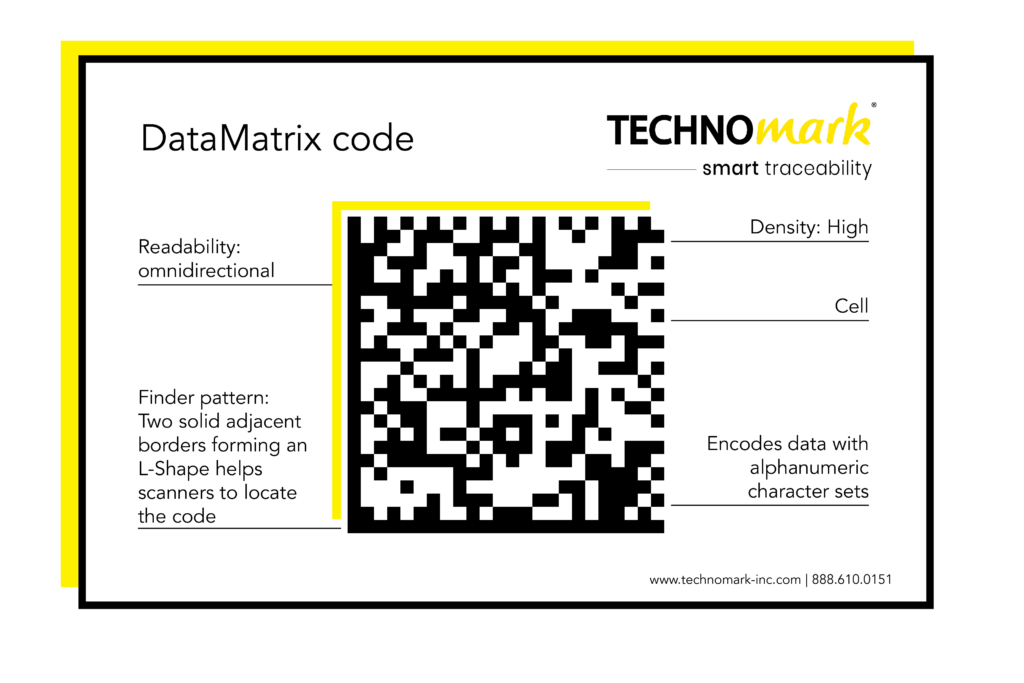
Have you ever wondered about the small, square barcodes often found on electronic devices, tools, and appliances? While they might resemble QR codes, they’re actually Data Matrix codes, essential components of modern manufacturing processes.
Unlike QR codes, primarily used for consumer-facing applications like websites and social media, Data Matrix codes are designed for efficient data storage and traceability. They’re the only 2D barcodes officially approved by GS1 for regulated healthcare items, emphasizing their reliability and accuracy.
QR codes on the other hand are larger and contain more data, such as website URLs, and can encode information in numeric and alphanumeric form as well as Kanji and other multi-byte character sets.
No matter what industry, when it comes to industrial traceability for manufacturers, choosing the right type of code can leave a production run riddled with misinformation and the chance of getting lost.
Let’s break down the differences and similarities between QR and Data Matrix codes and why the latter is the preferred choice of most manufacturers.
Understanding the distinctions between QR codes and Data Matrix codes is crucial for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes. Both codes are two-dimensional (2D) barcodes and consist of a pattern of squares that can be read by a barcode scanner. However, there are notable differences in their shape, size, and data capacity.
QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes scanned by smartphones or other devices with cameras. They store information in a matrix of black-and-white squares, which can be interpreted to reveal data such as URLs, text, or contact information. Think of them as digital links that can be quickly accessed by simply scanning them with your phone.

While both QR and Data Matrix codes are in the public domain and can be used royalty free, Data Matrix codes have become the standard for anti-counterfeit measures, part identification, and internal tracking because they feature advanced error-correcting techniques that are more robust than QR codes.
This presents a unique benefit for manufacturers that need to ensure their products can be identified if part of the mark gets damaged or impeded.
Particularly necessary for complex and high stakes industries such as medical, aerospace, and defense, where hundreds to thousands of components are needed in order to assemble a finished product, Data Matrix codes can be read even if up to 50% of the mark gets damaged.
QR codes on the other hand have steadily been adopted in consumer-facing applications. These codes can be found everywhere from business cards to product packaging, containing links to websites, resumes, premium offers, and even restaurant menus.
QR codes have a lower level error-correcting built in, and can be rendered useless with even slight ware and tare. Just 30% of a QR code needs to be damaged before it becomes unreadable.
While these codes are perfect for consumer-forward use, marking a component or part with a QR code presents a real danger for misidentification pending the mark gets damaged.
| Data Matrix |
|---|
| Supply chain traceability |
| Anti-counterfeiting through serialization |
| Part identification |
| QR code |
|---|
| Additional product information |
| Usage instructions |
| Social sharing |
| Auto-linking for spare ordering and registration |
| Promotions, contests, and gamification |
While Data Matrix codes are typically reserved for industrial use cases, both types of marks can play a role in the manufacturing industry.
Since both DataMatrix and QR codes are GS1 approved, they can carry any GS1 ID keys including:
| Used to Identify |
|---|
| Products and services |
| Parties and locations |
| Returnable assets |
| Assets |
| Service provider and recipient relationships |
| Components and parts |
| Product model |
| Example |
|---|
| Can of soup, chocolate bar, music album |
| Companies, warehouses, factories, stores |
| Pallet cases, crates, totes |
| Medical, manufacturing, transport and IT equipment |
| Loyalty scheme members, doctors at a hospital, library members |
| Automobile parts |
| Medical device |
Beyond GS1, specifications and requirements for each code are presented by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). For more about how these codes work themselves, and how to create them, you can check out the relevant ISO standard for more detail.
Requirements for Data Matrix codes are specified under the ISO/IEC 16022 international standard; while requirements for QR codes are specified under the ISO/IEC 18004 international standard.
Implementing Data Matrix codes in a manufacturing process can significantly enhance traceability, efficiency, and accuracy. However, to fully leverage the advantages of this technology, it’s crucial to follow best practices tailored to the specific needs of your operations.
Best practices for implementing Data Matrix codes include:
Data Matrix codes have more robust error-correcting features compared to QR codes. They can still be accurately read even when up to 50% of the code is damaged, making them more reliable in harsh environments like manufacturing or logistics. QR codes, on the other hand, lose readability once about 30% of the code is damaged, making them more prone to failure in industrial settings where wear and tear are common.
The cost of implementing QR or Data Matrix codes can vary depending on factors such as the specific hardware and software used, the complexity of the system, and the volume of codes needed. In general, Data Matrix codes may be slightly more expensive to implement due to the specialized equipment required for their reading and writing. However, the long-term benefits of using Data Matrix codes, such as improved traceability and efficiency, can often outweigh the initial costs.
While both QR and Data Matrix codes can be scanned at high speeds, Data Matrix codes often have a slight advantage in terms of scanning accuracy. Their smaller size and denser data encoding make them less prone to misreading, especially in challenging conditions.
Understanding the differences between QR codes and Data Matrix codes, and choosing which is best for your application can get overwhelming. That’s why its important to consult a trusted advisor and partner.
Technomark has been operating and supplying expertise with industrial marking equipment since 2000. Since 2018, Technomark North America has been the only established OEM of dot peen and laser marking systems — the primary methods for direct part marking — with a headquarters in the USA.
Technomark has been at the forefront of industrial marking innovation, developing machines for seamless integration in manufacturing processes.
Our goal is to help our customers:
Your relationship with Technomark North America shouldn’t be limited to a strict supplier-to-customer interaction. We value communication above all else, which is why our team is dedicated to finding ways to solve your traceability challenges through a consultative process.
Interested in learning more about Direct Part Marking using Laser Technology? Check out our free ebook below:
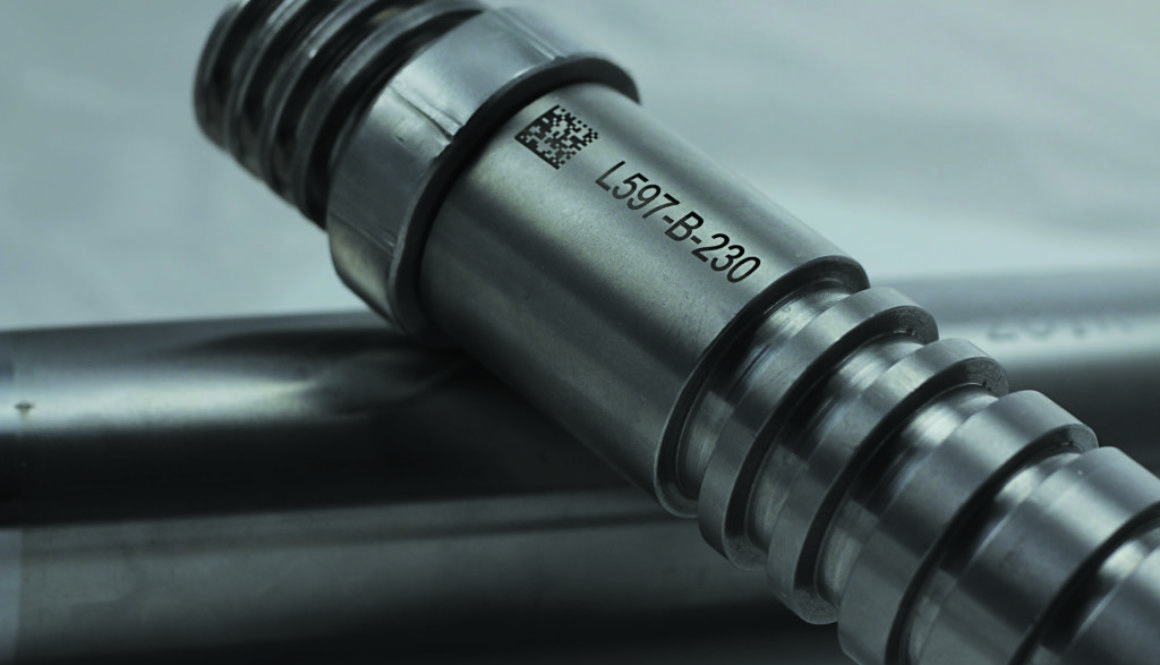

What commonalities do DVD players, checkout lines at the grocery store, and industrial marking machines all share? Lasers.
But alas, not all lasers are the same.
Do you know what L.A.S.E.R. stands for? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. In other words, it’s a highly concentrated beam of light. Lasers consist of a:

Part marking systems are crucial across various industries for tracking, identification, quality control, and regulatory compliance. Two popular methods for part marking are dot peen marking and laser marking. Each has its advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications based on factors such as material compatibility, precision, cost, and durability of the mark. Here’s a detailed discussion and comparison:
Dot peen marking involves a pneumatically or electromechanically driven pin that rapidly indents the material surface with dots to create numbers, letters, logos, or 2D Data Matrix codes. The resulting mark is a series of closely spaced dots forming lines or shapes.
This type of marking is widely used in automotive, metalworking, and aerospace for marking components where the durability of the mark is critical. This can range from the process of adding serial numbers on engine parts to VIN numbers and tool identification.
Dot peen is often preferred for harder materials and where surface deformation is not a concern, whereas laser marking offers broader material compatibility and is better for delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
Advantages of dot peen marking include:
Disadvantages of utilizing dot peen marking include:
Laser marking uses a high-intensity light beam to slightly alter or ablate the surface material, creating high-contrast marks without contacting the material.
Techniques include engraving, annealing, etching, and foaming, depending on the material and desired effect.

Laser marking is commonly used in:
Three main advantages of laser marking are as follows:
Meanwhile, some disadvantages of this marking system include:
Note: The size of the parts can also be a factor, as even huge parts can easily be marked with a handheld dot peen marking system, while lasers are not developed to the point they can be utilized for large parts.
Laser marking offers unparalleled precision and flexibility for a wide range of materials and applications, while dot peen marking provides a cost-effective, durable solution for simpler marking tasks.
The choice between dot peen and laser marking ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, including:
Laser marking and dot peen marking are both widely used in industrial applications for the permanent marking of parts and products, but they differ significantly in their mechanisms and outcomes.
Laser marking utilizes a high-intensity light beam to etch or mark the surface of a material, allowing for precise, high-resolution marks including barcodes, QR codes, and intricate graphics, while dot peen marking involves a pneumatically or electromechanically driven pin that physically impacts the surface to create dots forming numbers, letters, or simple logos. Both are useful in any number of industries – depending the needs and expectations of the product line in question.
Our Part Marking page offers a detailed look at the types of lasers and benefits of each, as well as the benefits of dot peen marking as an alternative. The guide also shares info on the type of mark needed and the materials you are marking during production. Take a look:

Ask anyone inside the industrial manufacturing industry – part-marking is crucial to component traceability when working with large quantities. And while several different types of part-marking exist, Dot Peen marking technology has been a preferred solution for many years.
At a high level, Dot Peen marking machines use either electromagnetic or pneumatic force to rapidly oscillate a stylus, in turn indenting the marks onto the surface of the part.
One of the advantages of Dot Peen is that it’s very flexible and can be used in either manual or fully automated production lines. A lot of the applications Dot Peen serves are manual applications, however, with modular Dot Peen systems, you can start with a portable system and later convert it to an in-line system for integration with fully automated production lines.
If you took apart a Dot Peen machine, one of the most important components you would find is a carbide or diamond-tip stylus.
The Dot peen process is considered a “low-stress” marking method because the mark is generated via material displacement rather than material removal. The carbide stylus strikes the material surface to produce the mark via a series of cold-formed stamped dots. Compared to Laser Marking Systems, Dot Peen does not induce thermal shock to the part surface since the material is cold-stamped rather than super-heated to produce the mark.
Dot Peen systems are commonly used by manufacturers in the aerospace and oil & gas industries where low-stress marking is required, such as tubular and flow control products that are exposed to extreme pressure differential in the oilfield.
Dot Peen marking is viable for material hardness up to 63 HRC. Typically, when a part hardness is greater than 63 HRC, laser marking systems are recommended.
All of Technomark’s Dot Peen machines rely on an electromagnetic solenoid to actuate the marking stylus. Dots are plotted in an X/Y plane via electronic control for precise placement of the Dot pattern. Using electromagnetic force versus pneumatic also provides a greater level of control of both the depth of the mark as well as the ability to mark contoured or complex surface.
Dot Peen marking machines are utilized in almost every industrial-goods manufacturing operation, including:
While these machines can run in-line and handle large quantities in an automated production environment, most are operated manually using a battery pack to go mobile.
The best Dot Peen marking machines utilize a fully electric design and that doesn’t require compressed air to operate. All Technomark Dot Peen marking machines feature an Intelligent Driving Impact (IDI) function that allows for marking on many different materials and finishes. The IDI function automatically adjusts and levels the stylus to the workpiece. Whether the part has a curved, wavy, or complex geometry, the stylus will follow the contour of the marking surface while maintaining a constant depth of high-quality marking throughout.
When structural integrity is crucial, Dot Peen marking provides a low-stress marking solution that removes no material during the part marking process.
One of the biggest benefits of a Dot Peen Marking Machine is its ability to efficiently produce marks compared to other marking systems. Other benefits of Dot Peen machines include:
Integrating a dot peen marking machine into your production line will improve the productivity and quality of the part-marking process.
New and exciting dot peen innovations are coming this fall. Be on the lookout for machines that feature:
If you have questions regarding Dot Peen machines or any part marking machines, contact us today. At Technomark North America, we have the experience to help you get the best solutions for your industrial marking needs.
(Editor’s Note: This blog was originally published in September 2021 and was updated in December 2023.)
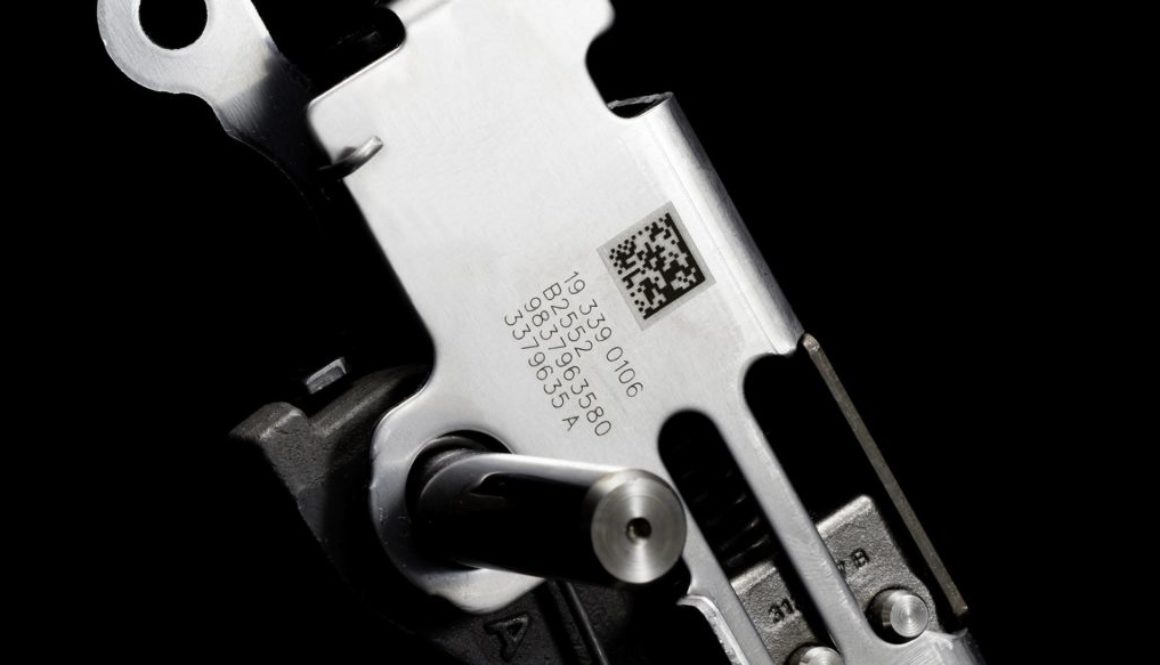

Commerce has come a long way from the bartering system. When currency became the acceptable medium of exchange, it only made sense that a better system of marking products was needed.
The first barcode was created in 1952, but they weren’t put into use in commerce and the transaction process until 1974, when a pack of Wrigley’s gum was scanned in a supermarket in the state of Ohio.
Barcodes have become widely used and have been upgraded and improved in an ongoing process. From the days when a barcode took up a significant amount of the packaging and contained limited information to today’s Data Matrix codes that are significantly smaller and can hold more data, the barcode development process has been fast and focused on efficiency.
Here we will focus on Data Matrix codes, their importance, their history, and an in-depth look at:

The technology associated with direct part marking has been steadily advancing over the years. Instead of having to be anchored to a workstation, users can now easily take their marking systems wherever they need them. This can be key for the food & beverage industry, for example, which is making a concerted effort to improve product traceability throughout supply chains.
It is also important for a variety of industries where dot peen machines reign supreme; the automotive, aerospace, medical, industrial, and defense industries, to name a few. With a variety of options for marking heads, it’s easier than ever to customize every setup. Furthermore, new systems make it easier to quickly and effectively mark parts with accuracy and precision while ensuring data integrity.
Electromagnetic dot peen markers provide a quick and reliable solution for direct part marking. This marking method can permanently identify parts without needing to be connected to a workstation. The portable, lightweight design makes it easy to set up and move the system even in tight spaces.
Electromagnetic dot peen markers are also highly accurate and precise with their marks, providing consistent readability over time. With advanced technology, users can customize their dot peen machine according to their needs while easily ensuring data integrity for each part marked.
When it comes to finding a reliable dot peen marker, it is important to not only look for the right features and quality in the product but also to consider the vendor. It is important to look for vendors who can provide support and services such as timely shipping, technical assistance when needed, and customer service.
It is also beneficial to find a vendor close to your physical location to minimize disruptions or delays in receiving the products. Finding a reliable vendor with these qualities can be essential for ensuring an effective dot peen marking process.
Reliability in a dot peen marking system is key to a successful production line from start to finish. Many industries, from automotive parts production to the medical field, require reliable traceability throughout the lifespan of the product.
Providing a reliable dot peen marking solution that does not require permanent installation at a specific location means you can potentially expand the product lines you manufacture and provide the same reliable marking solutions for all products.
A portable dot peen marking solution in today’s market should offer the following advantages:
Various products in separate production areas can be marked within a day’s work, provided via the device’s mobility.
The secure wifi control and capability to pair heads through serial number identification improves Buddy performance over comparable marking solutions.
A non-iOS smartphone within 10 meters can control the marking head, improving precision.
Products both indoors and outside can be marked by this dot peen marking machine, and the device allows marking on any surface of the product with the 360-degree adjustment potential.
The Buddy features the benefits noted above and also offers:
Choosing a portable dot peen marker to optimize your production and fit your portability needs can be a challenge. If you know what you’re looking for and are on the hunt for the best portable dot peen marking solution, our Technomark staff can help you check off the boxes on your list.
If you’re looking for traceability information, consider this resource:

Are you a manufacturing professional looking to stay ahead of the curve? If so, EASTEC 2023 is the event for you! This three-day conference and expo will allow attendees to learn from industry experts, explore new products and technologies, and gain valuable insights into modern manufacturing processes.
Technomark will be in Booth 3157 May 16-18 at the Eastern States Exposition in West Springfield, Mass. If you want to stop by and have parts marked live, registration for the event is open. Remember to register with Technomark’s promotional code: 16253977E. This will make badge creation free for those interested (normally $50).
Attendees will have access to industry-leading manufacturers and suppliers, allowing them to gain valuable insights into new products, processes, and technologies. In addition, EASTEC 2023 will feature interactive workshops, seminars, and panel discussions with industry experts.
The schedule for this year’s event includes a number of speakers:
There will also be four panel discussions, focused on:
Workshops during the upcoming EASTEC show will highlight the following areas:
EASTEC is a unique and remarkable manufacturing trade show that offers an opportunity to learn, explore and discover the latest advances in technology and manufacturing.
This event provides an excellent platform for attendees to learn from top leaders in their respective fields and network with others in the manufacturing community.
By attending EASTEC 2023, you will join thousands of other professionals in the manufacturing industry who are looking to stay ahead of the curve. With networking opportunities and the latest technological advancements, there’s something for everyone.
Not all of your time will be spent at the exhibits and workshops during EASTEC 2023. Once you have grabbed a bite to eat, consider one of these options for entertainment:
1. Visit the Springfield Museums to learn more about the history of Springfield and its diverse culture. Storrowton Village Museum, for example, offers insight into early 19th-century life.
2. Enjoy a scenic ride on the Springfield trolley along this vibrant city’s rivers, valleys, and historical sites. Visitors can explore numerous historical sites throughout the city that reflect this varied past, from the Springfield Armory National Historic Site, which preserves one of America’s most important military landmarks, to Duryea Way honoring James Duryea, who made significant contributions to automobile production during his lifetime.
3. Explore the Forest Park Zoo of Springfield and its many exotic animals. Located on the banks of the Connecticut River, this vibrant and educational zoo offers visitors an up-close look at some of nature’s most exotic creatures. From majestic tigers to tiny tree frogs, there are plenty of animals to observe and learn about in this unique setting. In addition to its impressive animal collection, the zoo also features interactive exhibits allowing visitors to get closer to their favorite creatures.
4. Visit the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame, located in Springfield. The museum offers information on more than 400 inductees and over 40,000 sq. ft. of basketball history – drawing more than 200,000 visitors each year.

When it comes to a CNC trade show, the right ones provide access to information on new technology and networking opportunities to connect with new suppliers. EASTEC 2023 provides these resources and more. Don’t forget to register! Technomark staff will be waiting at Booth 3157.
Our experienced staff is available to discuss all things part marking. If you want to learn about laser marking, consider reading through this resource:
"*" indicates required fields